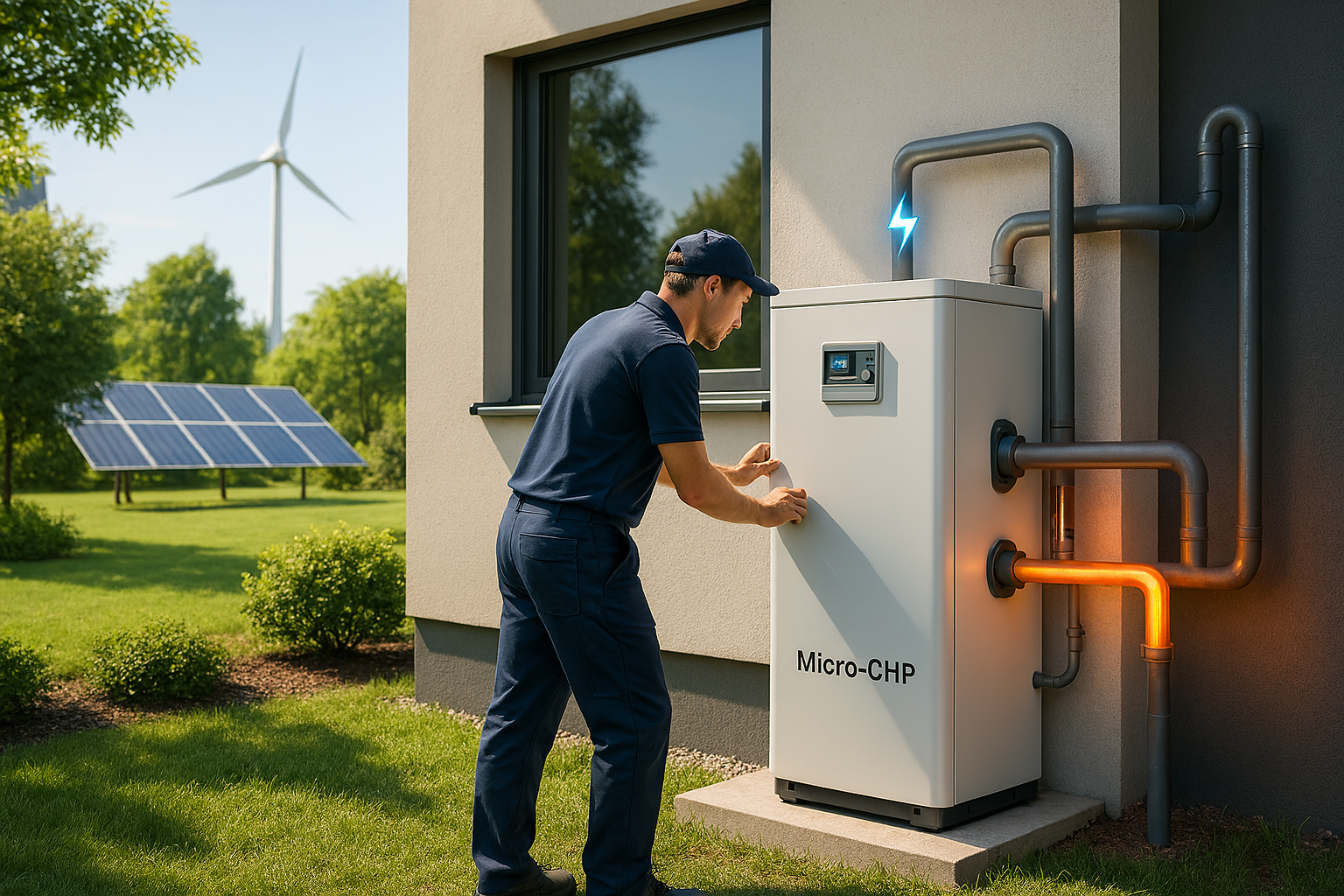
As global energy systems transition toward sustainability, Micro-CHP technology is emerging as a cornerstone of decentralized energy solutions. This powerful innovation is changing how we think about home and business energy. By simultaneously generating electricity and useful heat from one fuel source, Micro-CHP systems deliver exceptional efficiency. They often exceed 80% total efficiency while significantly reducing carbon emissions and overall energy costs. Governments worldwide now recognize this technology’s vast potential. They are integrating Micro-CHP into national energy strategies, offering incentives for adoption, and funding cutting-edge research. This blog explores the very latest developments from official government sources in the U.S., U.K., and E.U., highlighting how Micro-CHP is rapidly shaping the future of clean energy.
Why Micro-CHP is a Game Changer
Traditional power generation wastes significant energy as heat during the process of creating electricity. We essentially throw away a valuable resource. Micro-CHP systems solve this problem by capturing this otherwise wasted heat. They use the heat for residential or commercial space and water heating. This process achieves efficiencies far beyond conventional, separate heating and power methods.
For households, this translates directly to lower monthly utility bills. It also means reduced reliance on sometimes fragile centralized electricity grids. For industries and large businesses, this setup offers greater energy resilience and operational flexibility. These are critical factors in the current era of widespread electrification and urgent decarbonization efforts. This twin benefit of power and heat makes it exceptionally efficient.
🇺🇸 United States: The DOE’s Decarbonization Focus
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has strategically positioned Combined Heat and Power (CHP), which includes the micro-scale version, as a key pillar. This focus is part of its overarching Industrial Decarbonization Roadmap. The national strategy strongly emphasizes improving energy efficiency and integrating with low-carbon fuels. Fuels like biogas and clean hydrogen are central to this plan.
The DOE’s Advanced Manufacturing Office has identified several key R&D areas. These priorities include flexible CHP systems and high-efficiency gas turbines. They are also developing grid-responsive prime movers. These innovations aim to transform CHP into a truly resilient distributed energy resource. This resource will be fully capable of supporting local microgrids. It can also help stabilize power delivery during times of high peak demand.
The DOE ensures transparency through its Microgrid and CHP Installation Databases. These valuable public resources are updated monthly. They offer detailed insights into deployment trends across the country. The databases track installations ranging from small tens of kilowatts up to hundreds of megawatts. This information is vital for policymakers and energy investors alike.
A notable technological breakthrough occurred in March 2023. Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) successfully tested a residential Micro-CHP system. This innovative unit was powered by an opposed-piston internal combustion engine. This novel design promises significantly improved performance and system efficiency. It signals an exciting new era for smaller, residential-scale CHP solutions.
🇬🇧 United Kingdom: Policy and Financial Incentives
The U.K.’s Department for Energy Security & Net Zero (DESNZ) strongly underscores CHP’s efficiency in its national energy strategy. The department cites systems that achieve an impressive thermal efficiency of up to 80%. This can cut a user’s total energy costs by about 20% compared to traditional, separate setups.
To accelerate the adoption rate, the government introduced the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG). This smart policy compensates both households and businesses. They receive payment for exporting any surplus electricity generated from their Micro-CHP systems back to the main grid. This financial incentive applies to systems up to 50 kW in size. This makes Micro-CHP an exceptionally attractive option for small-scale users. These users seek both long-term sustainability and immediate financial returns.
🇪🇺 European Union: Fuel-Cell Micro-CHP Innovation
The European Union’s deep commitment to Micro-CHP is brilliantly exemplified by the PACE project. This major initiative received funding under the crucial Clean Hydrogen Partnership. Since its launch in 2016, PACE has successfully deployed over 2,500 highly advanced fuel-cell Micro-CHP units. These units are now operational across 10 different European countries.
The project has logged an impressive 23 million total operating hours. These powerful systems have delivered substantial energy cost savings for consumers. They have also significantly enhanced installer expertise across the continent. This is a critical step needed for achieving successful mainstream adoption.
In April 2023, PACE released a comprehensive, impactful policy briefing. This document urgently urged all national governments to integrate fuel-cell Micro-CHP into their long-term climate and energy plans. The briefing strongly emphasized the technology’s key role in multiple areas. These include reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving national energy security. It also perfectly complements intermittent renewable energy sources like wind and solar power. By smartly leveraging clean hydrogen as a primary fuel, fuel-cell Micro-CHP aligns perfectly with the EU’s ambitious decarbonization goals.
Key Factors Driving Micro-CHP Adoption
The movement toward widespread Micro-CHP adoption is being fueled by several simultaneous, powerful trends:
- Integration into Climate Frameworks: Governments worldwide are embedding Micro-CHP into their national, long-term energy strategies. They recognize its unique ability to deliver high efficiency and critical resilience.
- Targeted R&D and Innovation Support: Initiatives from the DOE and the E.U. are actively funding advanced technologies. These range from flexible CHP systems to sophisticated fuel-cell units. This ensures continuous, necessary performance improvements.
- Deployment Tracking and Incentives: Publicly available databases and financial schemes like the U.K.’s SEG offer transparency. They provide a strong financial motivation for consumers and businesses to adopt the technology.
- Proven Commercial Breakthroughs: Large-scale deployments, such as the PACE project’s 2,500 successful units, definitively validate its commercial readiness. They also clearly demonstrate tangible consumer benefits.
Remaining Challenges and Future Opportunities
While Micro-CHP offers numerous clear advantages, some challenges still remain for wider deployment. The initial installation costs for systems can sometimes be high. Widespread national adoption depends heavily on supportive, consistent government policies and increased consumer awareness. Fuel availability, particularly for the newer, hydrogen-based systems, also requires significant, upfront infrastructure development.
However, these hurdles should be viewed as opportunities for innovation and investment. They encourage powerful collaboration between government agencies, key industry players, and leading research institutions. The necessary infrastructure development will create new green jobs. Increased competition will naturally drive down the initial system costs over time.
The Promising Future Outlook
Micro-CHP is clearly poised to play an absolutely pivotal role in the ongoing global energy transition. As grid electrification accelerates and centralized grids face increasing strain, decentralized solutions will become essential. Technologies like Micro-CHP will provide the necessary resilience and energy efficiency. With strong, consistent policy backing, continued technological advancements, and growing consumer interest, the next decade looks bright. We could easily see Micro-CHP evolve from a current niche solution to a mainstream, universally adopted energy option for millions.
Final Thoughts on Micro-CHP
Micro-CHP is more than just a smart technology; it represents a comprehensive strategy for sustainable living and increased industrial competitiveness. By intelligently harnessing both heat and power in one integrated system, it simultaneously addresses three major concerns. It solves energy efficiency, achieves significant cost savings, and lowers our overall carbon footprint. Governments worldwide are placing significant bets on its enormous potential. The latest developments we have examined confirm that Micro-CHP is not merely a passing trend, it is a powerful, ongoing energy transformation.