Infrared sensors play a critical role in modern safety systems, offering significant benefits for homes, offices, and commercial environments. By detecting heat and light beyond the visible spectrum, these sensors sense movement, presence, and environmental changes accurately. Consequently, users experience enhanced security, smarter automation, and greater energy efficiency. This blog explores what infrared sensors are, how they operate, the different types available, their key applications, limitations, and essential installation and maintenance tips. Understanding these factors helps maximize their potential.
What Are Infrared Sensors?
It detects infrared radiation, which consists of electromagnetic waves beyond visible light. Objects naturally emit or reflect this radiation depending on their temperature and composition. When a sensor registers variations in infrared energy, it converts the readings into electrical signals that trigger alarms, devices, or other responses. Essentially, all objects above absolute zero produce some level of infrared radiation. By monitoring changes in this energy, sensors detect motion, heat, or presence within a space, enabling accurate and reliable monitoring.
How Infrared Sensors Work
Infrared sensors monitor a defined area by continuously measuring infrared radiation levels. When an object enters the field or moves, the sensor detects changes in thermal patterns. This detection triggers a response, such as activating lights, sending alerts, or initiating alarms. Some sensors integrate advanced processing to reduce false alarms caused by pets, shadows, or environmental fluctuations. In security systems, this process occurs in real time, providing instant feedback to operators and allowing rapid responses to intrusions or unusual activity. Their immediate action enhances safety and reduces potential threats effectively.
Types of Infrared Sensors
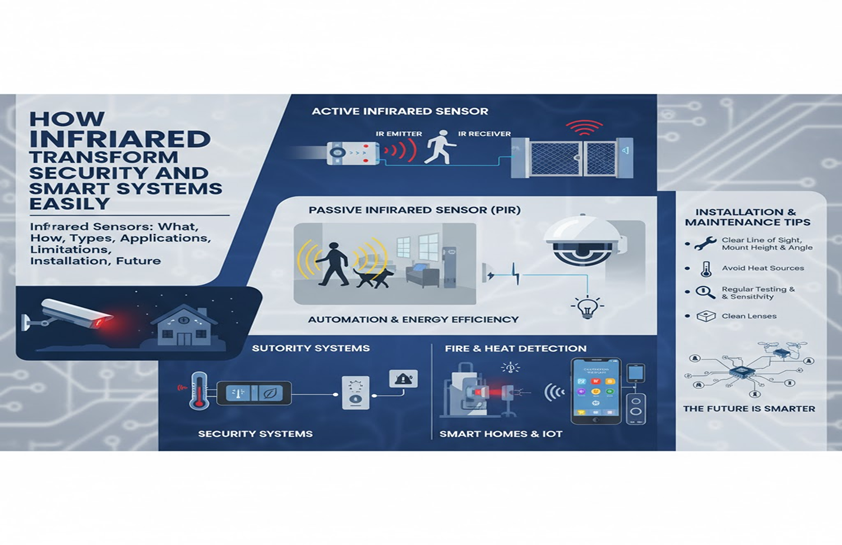
- Active Infrared Sensors: They use both an emitter and a receiver. The emitter sends infrared waves into the surrounding area, and the waves bounce back from objects to the receiver. By analyzing these reflections, the sensor determines the presence, distance, or movement of objects. These sensors are especially useful in beam or barrier systems, such as entrance monitoring or industrial safety setups, providing precise detection even in challenging conditions.
- Passive Infrared Sensors: Commonly known as PIR sensors, utilize only a receiver to detect natural infrared radiation. They monitor ambient thermal energy and respond when a warm object, such as a human or animal, enters the detection zone. PIR sensors are widely used in motion detection, energy-saving automation, and home security systems. They are energy-efficient since they do not emit infrared waves, and they are suitable for human presence detection in residential and commercial settings.
Applications of Infrared Sensors
- Security Systems: The sensors form the backbone of modern security systems by detecting unauthorized motion and triggering alarms. Integration with security cameras enhances night vision capabilities, ensuring detection even in complete darkness. They protect residential, commercial, and industrial spaces effectively, reducing reliance on manual monitoring.
- Automation and Energy Efficiency: Infrared sensors contribute to energy savings by detecting occupancy and automating lighting, HVAC, and other systems. They prevent energy waste by ensuring devices operate only when necessary. In commercial buildings, they optimize lighting schedules and improve operational efficiency. In smart homes, they enhance convenience and comfort, responding to human activity automatically.
- Fire and Heat Detection: Infrared sensors identify abnormal heat signatures, enabling early detection of fires or overheating equipment. Industrial settings rely on these sensors to monitor machinery, equipment, and critical systems, reducing the risks of accidents. Integration with fire alarm systems enhances workplace safety, providing timely warnings for emergency response.
- Smart Homes and IoT Integration: Infrared sensors integrate seamlessly into smart homes and IoT systems, enabling intelligent automation of lighting, climate control, and appliances. They detect occupancy and environmental changes, triggering devices based on real-time needs. This automation improves convenience, energy efficiency, and security simultaneously, creating responsive and adaptive living spaces.
Limitations of Infrared Sensors
Infrared sensors are highly effective, but environmental factors can reduce their accuracy. Extreme temperature changes, fog, smoke, or high humidity may affect detection. Placement is critical because obstructions such as furniture, walls, or plants can block the field of view. Passive sensors detect changes in heat rather than identifying objects, sometimes confusing pets or other warm objects with humans. Active sensors can experience performance issues if the emitter-receiver path is misaligned or obstructed. Understanding these limitations ensures realistic expectations and optimal sensor deployment.
Best Practices for Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation ensures reliable sensor operation and longevity. Place sensors with a clear line of sight and mount them at the recommended height and angle for the target area. Avoid positioning them near heat sources or vents that may trigger false alarms. Test sensors regularly to confirm proper function, adjust sensitivity as needed, and clean lenses to remove dust or debris. Inspect wiring and power connections to prevent downtime. Following these practices guarantees consistent performance and prolongs the system’s operational life.
The Future of Infrared Sensors
Infrared sensors continue to evolve, becoming smaller, more sensitive, and smarter with advanced signal processing. Future innovations will enable more complex detection, such as tracking movement patterns and distinguishing between different objects. Increasing automation and security demands will drive wider adoption in homes, offices, and industrial environments. As technology advances, infrared sensors will continue providing reliable, energy-efficient, and intelligent monitoring solutions for diverse applications.
Conclusion
Infrared sensors are foundational in modern detection systems, reliably sensing motion, heat, and presence. By understanding active and passive types, environmental considerations, and installation best practices, users can maximize performance. These sensors enhance security, enable automation, conserve energy, and integrate seamlessly into smart home and industrial systems. With careful planning and regular maintenance, infrared sensors act as silent guardians, continuously monitoring spaces and supporting intelligent automated responses that improve safety, convenience, and efficiency.