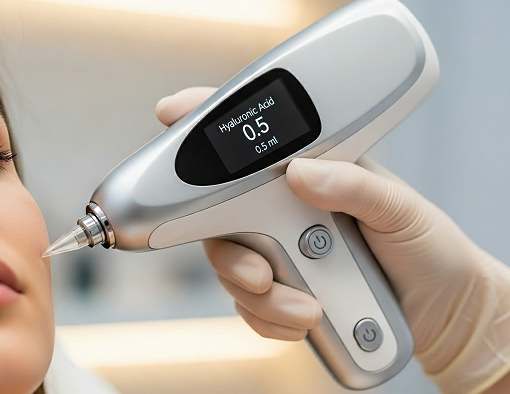
Aesthetic Injectable Devices
The realm of aesthetic medicine has transformed dramatically in just two decades. At the heart of this transformation are aesthetic injectable devices. These non-surgical tools, including dermal fillers, botulinum toxins, and biostimulants, deliver agents directly into skin or subcutaneous tissues in order to improve facial aesthetics. As a result, what was once considered a marginal niche has now gained significant acceptance among both patients and practitioners who seek non-invasive, safer, and customizable options for facial rejuvenation.
In clinical practice, practitioners use aesthetic injectable devices to administer materials like dermal fillers or neurotoxins into the skin. These treatments enhance facial features, minimize wrinkles, or add volume. To suit different needs, there are various types of aesthetic injectables, ranging from manual syringes to advanced automated devices.
Types of Aesthetic Injectable Devices
- Manual Syringes
A qualified professional injects manual syringes, the most basic tools, which consist of prefilled devices containing the desired product. - Automated Injector Devices
Devices such as the Vital Injector 2 from CliniMed Aesthetics offer greater control. They feature depth regulation and provide consistent injections through an automated delivery system. - Needle-Free Injectors
While not all are strictly aesthetic, some needle-free devices deliver substances into the skin using pressure or other mechanisms, eliminating the need for needles. - Multi-needle Injectors
Devices such as DermaPrecise use multiple needles to treat larger surface areas more efficiently, thereby reducing overall treatment time.
Popular Aesthetic Injectable Procedures
- Dermal Fillers
Manufacturers typically produce dermal fillers as gel-like substances made from materials like hyaluronic acid. These fillers help add volume, reduce wrinkles, and enhance facial contours. - Neurotoxins (e.g., Botox)
Neurotoxins work by relaxing targeted muscles, thereby reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. - Biostimulators
Biostimulators stimulate natural collagen production, which gradually improves skin texture and firmness over time.
Key Benefits
Thanks to technological progress, aesthetic injectables now offer a new level of precision and safety. Some of the main advantages include:
- Enhanced Precision: Digital controls ensure exact dosing and consistent injection depth, reducing the risk of complications.
- Minimized Discomfort: Automated delivery systems allow smoother, more even distribution, which helps reduce pain and swelling.
- Improved Safety: Safety features and feedback mechanisms significantly minimize the risk of human error.
- Time Efficiency: Faster procedures and shorter recovery times make these treatments ideal for busy individuals.
- Customization: Advanced technology allows treatments to be tailored based on patient factors like age, skin thickness, and treatment area.
Popular Substances Delivered via Injectable Devices
Aesthetic injectables can be grouped based on their function:
- Botulinum Toxins (e.g., Botox, Dysport, Xeomin)
These block nerve signals to muscles, reducing dynamic wrinkles such as crow’s feet and frown lines. - Dermal Fillers (e.g., Juvederm, Restylane)
These restore facial volume and smooth lines. Hyaluronic acid-based fillers are especially common due to their reversibility and safety. - Biostimulators (e.g., Sculptra, Radiesse)
These stimulate collagen production for longer-lasting, natural-looking results. - Skin Boosters (e.g., Profhilo, Rejuran)
These improve hydration, elasticity, and texture by delivering nourishing compounds into the dermis. - Fat-Dissolving Agents (e.g., Kybella)
These target and break down localized fat deposits, such as under the chin.
Recent Developments in Aesthetic Injectable Devices
Innovation continues to push boundaries in the aesthetic field. Notable updates include:
- March 24, 2025: Allergan Aesthetics (AbbVie) showcased its AA Signature program at the AMWC in Monaco, demonstrating how to elevate patient experiences and optimize treatment outcomes.
- June 5, 2025: Merz Aesthetics Canada received Health Canada approval for Radiesse in the décolleté area. With this approval, Radiesse, a regenerative biostimulator, has become more versatile. It promotes the regeneration of multiple components of skin tissue, resulting in healthier-looking skin.
- February 13, 2025: Evolus, Inc. announced FDA approval of Evolysse Form and Evolysse Smooth, the first HA gels in its new dermal filler collection. Consequently, Evolus now enters the U.S. HA dermal filler market, expanding its total addressable market by 78%—roughly $6 billion.
- September 2024: Allergan Aesthetics revealed that BOTOX Cosmetic was approved in China for treating masseter muscle prominence (MMP). This approval makes BOTOX the first neurotoxin approved in China for this indication, backed by clinical evidence and physician training.
- July 2024: Crescita Therapeutics signed an exclusive distribution agreement with NanoPass Technologies to launch MicronJet™600 in Canada. This collaboration aims to introduce advanced intradermal delivery in the medical aesthetics market.
- New Devices on the Market: Tools like Teosyal Pen and U225 Meso Injector utilize motorized systems to ensure consistent filler placement. Not only do these devices enhance accuracy, but they also minimize trauma in delicate treatment areas.
- Multi-needle Devices: Devices like Vital Injector 2 use several micro-needles to distribute skin boosters or vitamins across wider areas such as the cheeks, neck, or hands. These are particularly beneficial in mesotherapy, improving tone, hydration, and elasticity.
Safety and Regulation
As usage grows, so does the need for stringent regulation. In the U.S., the FDA oversees injectable devices, while in Europe, CE certification is required. Furthermore, practitioners must undergo extensive training—not just in device operation, but also in facial anatomy, emergency protocols, and patient safety.
Ultimately, the device itself matters less than the practitioner’s technique and judgment. Proper handling helps mitigate side effects like bruising, swelling, or rare but serious complications like vascular occlusion.
Final Thoughts
Aesthetic injectable devices sit at the crossroads of beauty, technology, and medicine. With each innovation, these tools continue to improve outcomes for patients while simplifying procedures for practitioners.
That said, the sophistication of a device means little without skilled hands and ethical practice. Therefore, comprehensive training, patient education, and clinical responsibility remain paramount.
As the demand for non-surgical aesthetic enhancement grows, injectable devices are set to lead the charge—offering millions of individuals smoother, safer, and more satisfying results.