Russian Energy
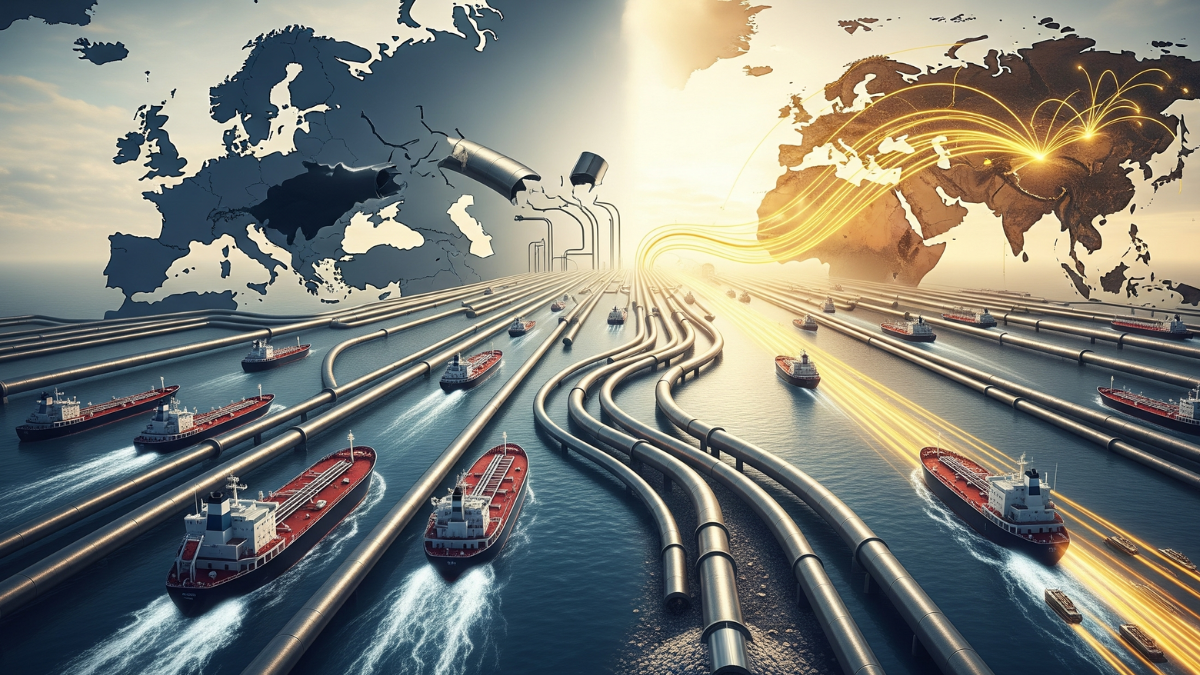
Russian energy exports remain resilient despite Western sanctions. Trade has shifted mainly to Asian markets, affecting global prices. Since early 2022, after the Ukraine invasion, Russia’s oil exports to Europe fell from over half to about 11% by mid-2025. Meanwhile, China and India significantly increased imports, with China buying 2 million barrels daily and India 1.6 million barrels.
Several factors explain this shift. First, key Asian countries have not sanctioned Russian fossil fuels, allowing direct imports. Second, Russia uses alternative supply chains and “shadow” tankers to bypass sanctions and keep volumes stable. Also, Russian liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports to Europe slightly rose despite pipeline declines. The EU imposed an 18th sanctions package in mid-2025, tightening price caps and import limits.
Despite these hurdles, Russian fossil fuel exports grew by 8% in volume in Q2 2025 versus earlier months. However, revenue dropped 18% year-on-year due to price caps and discounts. Crude oil prices rebounded modestly in mid-2025, softening revenue losses. G7+ tankers’ share in Russian oil shipping rose from 35% in early 2025 to 56% by June, showing rising enforcement complexity.
This export shift has major global effects. Discounted Russian oil pushes global prices down, impacting producers worldwide. It’s spread to Asia, offering cheaper fuel, changing trade patterns. Western sanctions and price caps target cutting Russia’s revenue to weaken its geopolitical power, but have only partly reduced exports.
The Russian energy export scene shows an ongoing clash between geopolitics and energy demand. Sanctions limit old export routes, yet Russia’s pivot to Asia and adaptive tactics keep supplies flowing. This sustains Russia’s influence over global prices and supply stability. Future results depend on sanction enforcement, price cap changes, and energy consumer shifts.
In sum, Russian energy exports stay strong through market shifts and adaptive logistics despite heavy sanctions. This resilience shapes global prices, sustaining competitive cost levels and complicating efforts to isolate Russian energy markets.